Staying ahead in fleet management requires a deep understanding of the core principles and tools that can make or break your operations. In this guide, we’ll explore the fundamental concept of fleet management and how a fleet manager leads it, the role of fleet management systems and software, and how technology can revolutionize various aspects of your fleet operations. You’ll soon be able to answer the question “what is fleet management?” in your own words and experience.
What is Fleet Management?
Fleet management, at its core, is the strategic coordination and supervision of a company’s vehicle and equipment fleet. It involves the strategic planning, organization, monitoring, and control of a group of vehicles used for various business purposes, such as transportation, delivery, or field services.
What Activities Does it Include?
Fleet management encompasses a wide range of activities and responsibilities, including:
- Vehicle Acquisition and Disposal: Deciding when to purchase, lease, or retire vehicles in the fleet. This includes selecting the right types of vehicles to meet the organization’s needs and budget.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Implementing regular maintenance schedules to ensure the fleet’s vehicles are safe, reliable, and compliant with regulations. This also involves managing repairs and minimizing downtime.
- Driver Management: Recruiting, training, and managing drivers to ensure they adhere to safety standards, follow company policies, and operate vehicles efficiently.
- Fuel Management: Controlling fuel costs by monitoring fuel consumption, reducing idling time, and implementing fuel-efficient practices.
- Route Optimization: Using software and data analysis to plan and optimize routes, which can reduce fuel consumption, travel time, and vehicle wear and tear.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Ensuring that the fleet complies with legal regulations, including vehicle inspections, emissions standards, and driver hours of service.
- Inventory and Equipment Management: Managing the inventory of spare parts, tools, and equipment necessary for vehicle maintenance and repair.
- Safety and Risk Management: Implementing safety protocols, monitoring driver behavior, and reducing the risk of accidents and liabilities associated with the fleet.
- Cost Control: Managing costs associated with vehicle ownership, operation, and maintenance to maximize profitability and budget efficiency.
- Data Analysis and Reporting: Collecting and analyzing data related to fleet operations to make informed decisions, improve performance, and identify areas for optimization.
- Environmental and Sustainability Initiatives: Implementing eco-friendly practices and technologies to reduce the fleet’s environmental impact, such as adopting hybrid or electric vehicles and minimizing emissions.
Why is it Important?
Fleet management is essential for businesses that rely on a fleet of vehicles as a core component of their operations, such as last-mile delivery companies, utility organizations, construction firms, and field service providers. Efficient fleet management not only helps reduce operational costs but also enhances safety, customer service, driver/operator recruitment and retention, and overall fleet productivity. It plays a crucial role in ensuring that a company’s vehicles are well-maintained, compliant with regulations, and contributes positively to the organization’s goals.

What Does a Fleet Manager Do?
A fleet manager plays a pivotal role in overseeing and optimizing the operations of a company’s vehicle and equipment fleet. Their responsibilities encompass a wide range of tasks and activities to ensure that the fleet is efficient, cost-effective, safe, and compliant with regulatory requirements. A fleet manager typically plays a significant role in determining and selecting the fleet management system (FMS) for their organization.
A fleet management system is a holistic approach to managing a fleet of vehicles. It involves the use of technology, data, and processes to optimize fleet operations. These systems often incorporate GPS tracking, remote diagnostics, and real-time monitoring to provide a comprehensive view of your fleet’s activities. The choice of a FMS is crucial because it directly affects the efficiency, safety, and overall management of the fleet. Here’s how a fleet manager is typically involved in the process of selecting an FMS:
- Needs Assessment: The fleet manager begins by assessing the specific needs and requirements of the organization’s fleet. This involves understanding the size of the fleet, types of vehicles, operational goals, and any existing challenges or pain points.
- Defining Objectives: Based on the needs assessment, the fleet manager helps define the objectives and goals of implementing an FMS. These objectives may include improving route optimization, enhancing driver safety, reducing fuel consumption, or achieving better maintenance management.
- Vendor Research: Fleet managers research various FMS vendors and solutions available in the market. They evaluate the features, capabilities, and pricing of different systems to identify potential options.
- Budgeting: Fleet managers work with the organization’s financial department to establish a budget for implementing an FMS. They consider the costs associated with hardware, software, installation, ongoing subscription fees, and training.
- Vendor Selection: After narrowing down the options, the fleet manager may lead the selection process, which often involves requesting proposals or quotes from FMS vendors. They evaluate proposals based on how well they align with the organization’s needs and objectives.
- Demo and Testing: Fleet managers may arrange demonstrations or trials of shortlisted FMS solutions to assess their usability and functionality in a real-world context. This helps in making an informed decision.
- ROI Analysis: Fleet managers conduct a return on investment (ROI) analysis to determine the potential cost savings and benefits that each FMS can offer. This analysis helps justify the investment to the organization’s decision-makers.
- Implementation Planning: Once the FMS is selected, the fleet manager works closely with the chosen vendor to plan the implementation process. This includes setting up hardware, configuring software, and training staff.
- Monitoring and Optimization: After implementation, the fleet manager is responsible for monitoring the system’s performance and ensuring that it meets the organization’s goals. They may also make adjustments and optimizations as needed.
- User Training: Fleet managers coordinate the training of staff and drivers on how to use the FMS effectively. This includes educating them on features like route optimization, driver behavior monitoring, and reporting.
While fleet managers have a significant say in the selection of the fleet management system, the decision should involve input and approval from other stakeholders within the organization, such as the IT department, finance department, and executive leadership. Ultimately, the goal is to choose an FMS that aligns with the organization’s objectives, fits within the budget, and enhances overall fleet operations. Buy in from organizational stakeholders will support the best possible management of key performance indicators (KPIs). Fleet leaders can get more on what KPIs they should be tracking in episode 17 of the Straight Talk on Fleet, hosted by award-winning fleet leader Erin Gilchrist.

How Does Fleet Management Work?
Fleet management, when done successfully, results in improved efficiency, reduced costs, enhanced safety, better compliance, and overall optimization of the organization’s vehicle fleet. Here are some of the key outcomes of effective fleet management, starting with safety. When safety is the focus, success in other areas will follow.
Enhanced Safety:
- Improved driver behavior through monitoring and feedback.
- Reduction in accidents and associated costs.
- Compliance with safety regulations and industry standards.
- Implementation of safety training programs for drivers.
- Prioritization from the organization on driver/operator safety.
Increased Efficiency:
- Routes are optimized, reducing unnecessary mileage and travel time.
- Vehicle downtime is minimized through proactive maintenance scheduling.
- Inventory management ensures that necessary parts and supplies are readily available.
- Real-time data analysis allows for quick decision-making and adjustments to operations.
Cost Reduction:
- Lower fuel costs due to optimized routes and reduced idle time.
- Decreased maintenance and repair expenses through preventive and proactive measures.
- Reduced insurance premiums as a result of improved driver safety.
- Better control over overall fleet-related expenses.
Better Compliance:
- Ensuring that the fleet adheres to legal and regulatory requirements.
- Keeping up with vehicle inspections, emissions standards, and driver hours of service.
- Minimizing the risk of fines and penalties associated with non-compliance.
Optimized Vehicle Lifecycle:
- Extending the lifespan of fleet vehicles through regular maintenance.
- Making informed decisions about vehicle acquisition and disposal.
- Maximizing the value of assets by keeping them in good condition.
Improved Customer Service:
- Timely deliveries and services due to optimized routes and accurate tracking.
- Providing customers with real-time updates and delivery estimates.
- Efficient response to customer inquiries and issues.
Data-Driven Decision-Making:
- Utilizing data analytics to make informed decisions and identify areas for improvement.
- Generating reports on fleet performance, costs, and key metrics.
- Continuously optimizing operations based on data insights.
Environmental Sustainability:
- Reducing the fleet’s carbon footprint through eco-friendly practices.
- Exploring light-weighting vehicles and most efficient assets for the job.
- Aligning with corporate sustainability goals.
Overall Organizational Benefits:
- Seen as a profit generator versus a cost center due to success from the above.
- Enhanced reputation for prioritizing driver/operator safety.
- Efficient fleet management supports the organization’s broader goals and objectives.
In summary, effective fleet management involves a strategic and holistic approach to managing a company’s vehicle fleet. It aims to optimize various aspects of fleet operations, including maintenance, routing, safety, compliance, and cost control. When executed well, fleet management leads to improved efficiency, reduced expenses, enhanced safety, and overall alignment with the organization’s goals. It is a dynamic and data-driven process that evolves to meet changing needs and challenges in the world of transportation and logistics.

What are the Benefits of Fleet Management?
Benefits for Customer Services
Effective fleet management enhances customer service in several ways. Timely deliveries, accurate tracking information, and efficient routes lead to improved customer satisfaction. With real-time data, you can provide customers with accurate delivery estimates and handle inquiries more efficiently.
Benefits for Maintenance and Vehicle Life
Proactive maintenance is a cornerstone of fleet management. Fleet management systems and software help track vehicle maintenance schedules, reducing breakdowns and extending vehicle life. Regular maintenance not only saves costs but also ensures the safety of your drivers.
Benefits for Driver Safety
Driver safety is a top priority for any fleet manager. Fleet management systems monitor driver behavior, providing insights into speeding, harsh braking, and other risky actions. By addressing these issues, you can enhance driver safety, reduce accidents, and lower insurance premiums.
Benefits for Operational Efficiency
Efficiency is the key to profitability in fleet management. Fleet management software optimizes routes, reduces idle time, and minimizes fuel wastage. It also helps with inventory management, ensuring that you have the right parts and supplies when needed.

How Does Fleet Management Software Help?
Fleet management software is the backbone of a fleet management system. It’s a suite of applications designed to streamline and automate various aspects of fleet operations. This software can include modules for maintenance scheduling, route optimization, fuel management, and more.
Your Options in the Market
Software for fleet management is a step up from using paper-based methods. It helps with accuracy, efficiency, and reporting. The outcomes are time and cost savings as well as insights to improve safety and operations of your fleet. But not all software is the same. Generally, fleet management software falls into the category of point solutions or lightly integrated solutions.
A point solution addresses just one aspect and doesn’t integrate with other tools. A lightly integrated solution gives an element of connection – sometimes as far as a single sign on for multiple solutions – but doesn’t integrate data. In both cases, these give you very limited management improvements and extra hurdles for usage and reporting. Data silos are not effectively knocked down and comprehensive insights are not available. This is where single connected platform excels.
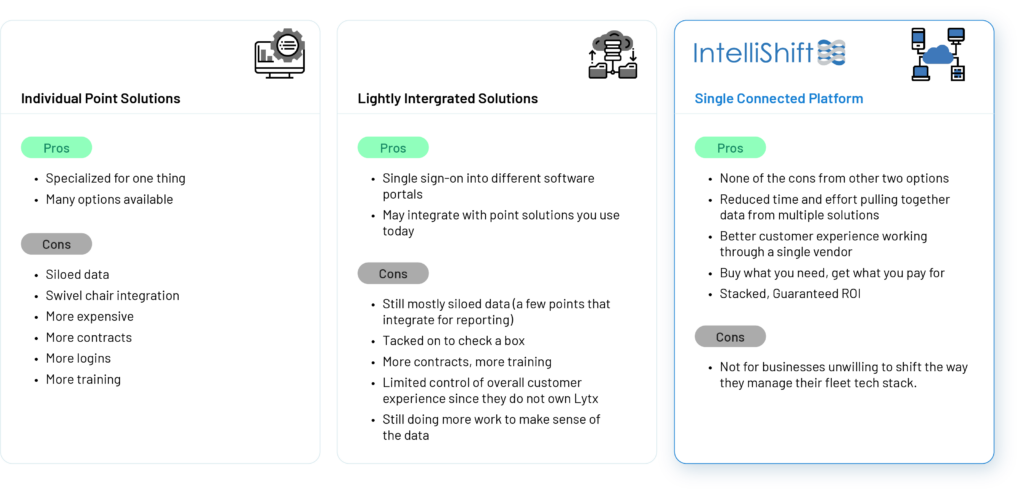
IntelliShift: A Single Connected Platform Optimizing Fleet Management
Implementing a comprehensive fleet management software system such as IntelliShift offers numerous advantages over traditional paper-based systems, single-point, or lightly integrated solutions. Here are the key improvements that fleet managers can expect:
- Centralized Data and Information: IntelliShift consolidates all fleet-related data into a single platform, providing real-time access to vital information. This eliminates the need to sift through paper records or manage multiple separate systems.
- Efficient Data Entry and Retrieval: Data entry is streamlined, reducing manual record-keeping. Users can quickly input data and retrieve information, saving time and minimizing errors.
- Real-Time Tracking and Monitoring: IntelliShift offers real-time tracking of vehicle locations, driver behavior, and vehicle health. Fleet managers can make informed decisions based on up-to-the-minute data.
- Comprehensive Reporting: IntelliShift generates detailed reports on various aspects of fleet operations, such as fuel consumption, maintenance schedules, driver performance, and compliance. These reports provide valuable insights for decision-making and compliance management.
- Route Optimization: IntelliShift optimizes routes, reducing mileage and travel time. This leads to fuel savings, improved delivery times, and increased efficiency compared to manual route planning.
- Maintenance Scheduling and Alerts: IntelliShift includes maintenance scheduling features that track service intervals and send automated alerts when maintenance is due. This proactive approach minimizes vehicle breakdowns and extends vehicle life.
- Cost Control: Fleet managers can closely monitor and control costs through expense tracking and analysis provided by IntelliShift. This includes fuel costs, maintenance expenses, and vehicle acquisition costs.
- Driver Behavior Monitoring: IntelliShift monitors driver behavior, identifying unsafe practices such as speeding, harsh braking, and excessive idling. This encourages safer driving habits, reduces accidents, and lowers insurance premiums.
- Inventory Management: IntelliShift helps manage inventory by tracking spare parts and equipment needed for vehicle maintenance. This ensures that the right parts are available when needed, minimizing downtime.
- Integration with Other Systems: IntelliShift can integrate with other systems, such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) or financial software. This seamless integration streamlines operations and data flow across the organization.
- Scalability: IntelliShift can easily adapt to the growth of the fleet, making it scalable for businesses with changing needs.
- Environmental Impact Reduction: IntelliShift can contribute to environmental sustainability by optimizing routes, reducing fuel consumption, and minimizing emissions, aligning with corporate sustainability goals.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: IntelliShift has a user-friendly interface that is easy for fleet managers and staff to navigate, reducing the learning curve.
- Regulatory Compliance: IntelliShift assists in maintaining compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards, reducing the risk of non-compliance-related penalties and fines.
The Biggest Advantage: Fleet Intelligence
Through centralized data and comprehensive reporting, management gets true fleet intelligence, which offers a holistic view of the entire fleet’s performance. It enables fleet managers to optimize routes, minimize fuel consumption, and proactively schedule maintenance, resulting in significant cost savings and improved operational efficiency. With the ability to monitor driver behavior and vehicle health in real-time, fleet intelligence helps ensure a safer work environment, reducing accidents and insurance premiums.
Overall, comprehensive fleet management software like IntelliShift significantly enhances the efficiency, transparency, and effectiveness of fleet operations compared to paper-based systems or single-point solutions. It empowers fleet managers with the tools and data they need to make informed decisions, reduce costs, enhance safety, and streamline overall fleet management processes.





![Episode 50 Thumbnail Erin celebrates building the fleet community with 50 episodes and 11K followers on LinkedIn [Podcast]](https://intellishift.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/WhatisFleetManagement-Guide-Cover.jpg)



